Lungs Cancer is a serious health condition that affects thousands of individuals worldwide. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of lung cancer, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer begins when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in one or both lungs. These cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, making early detection and treatment crucial for improving outcomes.
Types of Lung Cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of all cases. It includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is less common but tends to spread more quickly than NSCLC. It is often associated with heavy smokers and comprises about 15% of lung cancer cases.
Causes and Risk Factors
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. The risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked and the duration of smoking.
Secondhand Smoke
Exposure to secondhand smoke can also increase the risk of lung cancer, especially for nonsmokers who live or work with smokers.
Radon Exposure
Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, is another significant risk factor for lung cancer. It can accumulate in homes and buildings, particularly in areas with high levels of uranium in the soil.
Occupational Exposure
Certain occupations, such as mining, construction, and industrial work, expose workers to carcinogens like asbestos and diesel exhaust, increasing their risk of developing lung cancer.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of lung cancer may include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing, hoarseness, and coughing up blood.
When to See a Doctor
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any persistent symptoms, especially if you have a history of smoking or other risk factors.
Screening Recommendations
Screening for lung cancer with low-dose CT scans is recommended for individuals at high risk, such as current or former smokers.
Diagnosis
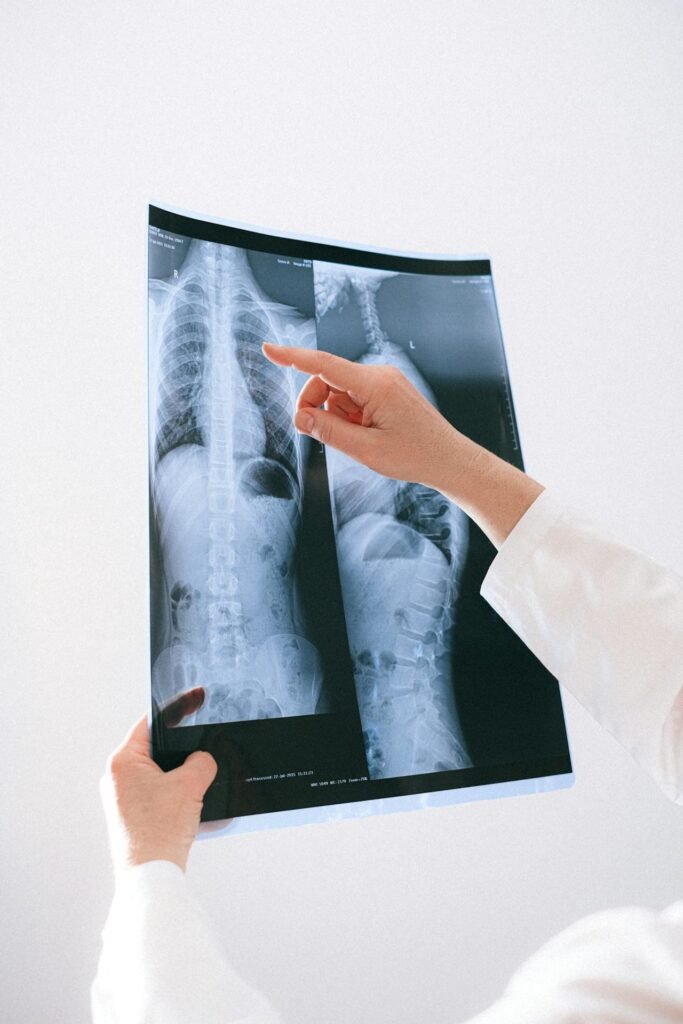
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like CT scans, PET scans, and X-rays help doctors visualize abnormalities in the lungs that may indicate cancer.
Biopsy and Pathology
A biopsy involves taking a tissue sample from the lung for examination under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Staging
Staging determines the extent and spread of cancer, guiding treatment decisions and prognosis.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery may be an option for early-stage lung cancer to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors, often used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body, particularly effective for cancers that have spread beyond the lungs.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy targets specific genetic mutations in cancer cells, disrupting their growth and spread.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells, offering new hope for treating advanced lung cancer.
Living with Lung Cancer
Coping Strategies
Coping with lung cancer involves emotional support, lifestyle adjustments, and open communication with healthcare providers and loved ones.
Support Systems
Support groups, counseling services, and palliative care can provide invaluable support for patients and their families throughout the cancer journey.
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet, can improve overall well-being and treatment outcomes.
Prevention
Smoking Cessation Programs
Quitting smoking is the single most effective way to reduce the risk of lung cancer and improve overall health.
Avoiding Secondhand Smoke
Minimizing exposure to secondhand smoke at home, work, and public places can lower the risk of developing lung cancer.
Radon Testing and Mitigation
Testing homes for radon and implementing mitigation measures if high levels are detected can reduce exposure and lower the risk of lung cancer.
Occupational Safety Measures
Employers and workers should follow safety protocols to minimize exposure to carcinogens in the workplace, such as wearing protective equipment and ensuring proper ventilation.
Latest Research and Innovations
Clinical Trials
Ongoing research and clinical trials offer new insights and treatment options for lung cancer, encouraging patients to explore participation in clinical trials as part of their care plan.
Advances in Treatment
Advancements in molecular testing, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy continue to improve outcomes and quality of life for lung cancer patients.
Support Resources
Organizations and Support Groups
Organizations like the American Lung Association and Lung Cancer Foundation provide resources, advocacy, and support for patients and caregivers.
Online Resources
Websites and online communities offer information, forums, and virtual support networks for individuals affected by lung cancer.
Conclusion
Lung cancer remains a significant health challenge worldwide, but advancements in early detection, treatment options, and supportive care are offering hope and improving outcomes for patients. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available resources, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and well-being.